Contents
Introduction to Cornea
Definition of the cornea: The cornea is the outermost layer of the eye. It is the transparent, domeshaped part that covers the exterior of the eye. In simple meaning, it is the clear exterior surface of the eye. It lies right in front of the iris and pupil, and it enables light to enter the eye.
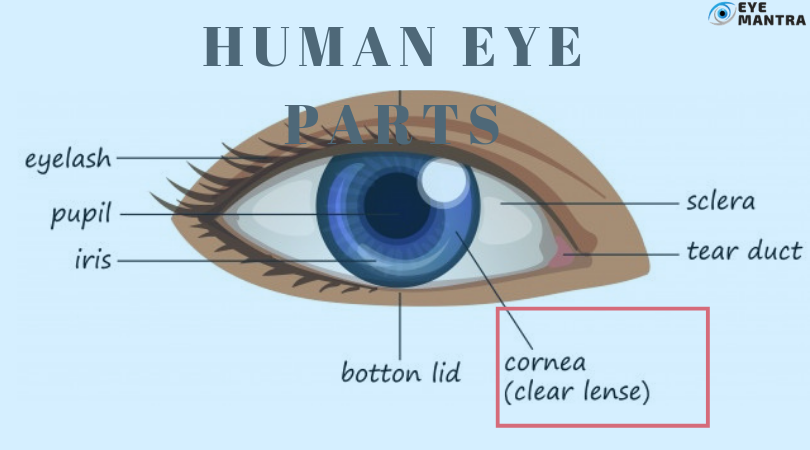
Even, it is one of the essential elements of the human eye as it allows the light to enter into the eye for creating a vision. As light enters your eye, it gets refracted or bent through the cornea’s curved edge. Cornea’s outer layer is basically a protective layer cornea. Along with the sclera, it works as a barrier versus dirt, germs, and other elements that can cause harm to the eye. This helps decide how well your eye can centre on objects close-up and far away. It is usually 12mm in length and 11mm in height.
Refractive difficulties like myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism are produced due to a change in the shape of the cornea.
If your cornea is harmed by disease, infection, or an eye injury, the resulting marks can affect your vision. They might block or bend light as it enters your eye.
Structure of Cornea
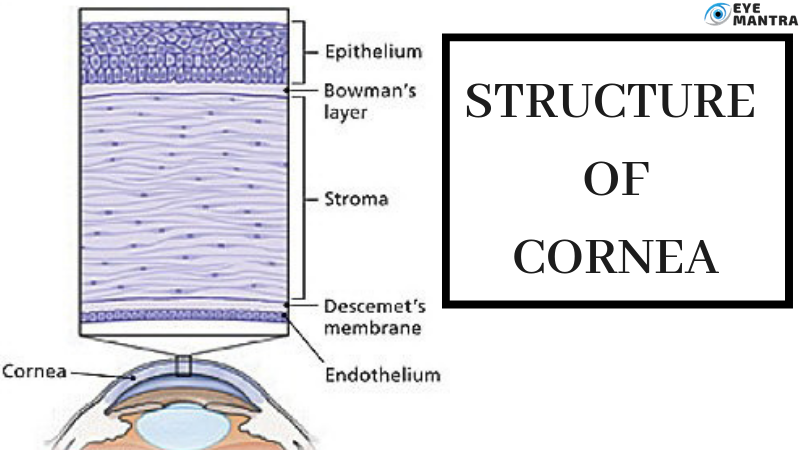
Even the cornea may seem clear and appear to lack substance, it is an extremely organized tissue. Unlike most tissues in the body, the cornea holds no blood vessels to nourish or protect it upon infection. Alternatively, the cornea gets its nourishment from tears and the aqueous humour.
The tissues of the cornea are designed in 3 basic layers, with 2 thinner layers, or membranes, among them. Each of the 5 layers has an essential function.
-
Epithelium – Retains the Eye Healthy
The epithelium is the cornea’s outermost layer. Also, it is loaded with 1000s of tiny nerve endings, which is why your eye may damage when it is scratched or rubbed. The section of the epithelium that epithelial cells support and prepare themselves to is named as the “basement membrane”.
Its main functions are to:
- Block the way into the eye of foreign material like dust, water, and bacteria, germs etc.
- Give a smooth surface to consume oxygen and nutrients from tears, which are then spread to the other layers of the cornea.
-
Bowman’s Layer – Safeguards the Eye
The next layer behind the basement membrane of the epithelium is a thin film of tissue called Bowman’s layer. It is also known as the anterior limiting membrane and is made up of protein fibres which are called collagen. It is a powerful layer that is among the epithelium and the corneal stroma and is created to protect the stroma.
-
Stroma – Provides a perfection for clarity
Behind Bowman’s layer is the stroma, which is the thickest layer of the cornea. It contains largely of collagen fibrils and water along with interconnected keratocytes which are used for the repair and support of the cornea. The unique shape, design, and spacing of collagen proteins are crucial in generating the cornea’s light-conducting clarity.
-
Descemet’s Membrane – Preserves from Infection
Behind the stroma is Descemet’s membrane, a light but strong film of tissue that works as a protecting hurdle upon infection and injuries. This membrane is made of collagen fibres that are distinct from those of the stroma, and are produced by cells in the endothelial layer of the cornea. Also, it improves itself quickly after an injury. It is also recognised as a posterior limiting membrane.
-
Endothelium – Manages the Fluids
The endothelium is the thin, deep interior layer of the cornea. Endothelial cells are essential in maintaining the cornea clear. Usually, fluid flows gently from inside the eye into the stroma. The endothelium’s initial task is to pump this excess fluid out of the stroma. Without this pumping effect, the stroma can swell with water and grow thick and dark.
A healthy eye has a perfect perfect balance among the fluids floating in and out of the cornea at every time. Unlike the cells in Descemet’s membrane where the endothelial cells damaged by disease or injury that cannot be repaired or fixed.
Symptoms and signs of Cornea Problems
The term corneal disease leads to various conditions that change the cornea shape of your eye. These involve infections, tissue breakdown, and other diseases you get from your parents.
Your cornea normally heals itself after most minor injuries or diseases. But throughout the healing process, you may notice symptoms like:
- Eye Pain
- Blurred vision
- Tearing
- Redness in eyes
- Intense sensitivity to light
- Dry eyes
- Headache, nausea, fatigue
These symptoms also come with different eye problems, so they may signal a major issue that needs special treatment. You must consult a top eye doctor if you find these symptoms, they may suggest cornea surgery.
Cornea Problems
There are many problems that can affect the health of a cornea. Some of them are:
- Corneal Ulcer
A corneal ulcer usually happens as a painful, red eye, with moderate to critical eye discharge and reduced vision.
The disease results from a localized infection of the cornea, related to an abscess.
A corneal abrasion disturbs the protecting outer layer of cells of the cornea i.e. corneal epithelium, forming an open injury that raises your risk of a severe eye infection. So, it’s essential to see an eye doctor quickly if you found having corneal abrasion.
- Keratoconus
Keratoconus is a growing eye disease in which the normally round cornea thins and starts to swell into a cone-like shape. This cone shape turns light since it enters the eye on its way to the light-sensitive retina, creating a distorted vision.
- Corneal dystrophy
Fuchs’ dystrophy is an eye disease in which the inner layer of cells in the cornea experiences degenerative changes. This cell layer, called the endothelium, is accountable for keeping the precise volume of fluid in the cornea. The endothelium holds the cornea clear for good vision by pumping out excess fluid that can create corneal swelling.
- Dry Eyes
Though the cause of dry eyes typically occurs in the tears gland and eyelids, it can start to damage of the corneal epithelium, which creates eye distress and vision changes.
- Corneal Degeneration
While a few of these problems are not so severe but some of them might need a corneal transplant as they can be responsible for causing the corneal blindness in people.
There are many more eye problems like Corneal ulcer, Acanthamoeba keratitis, Fungal keratitis, Corneal ectasia and Chalazion. But the above mentioned are the common and major eye problems.
Treatment & Cost of Cornea problems
The cornea problems cab be easily cured by the following process ;
- Laser Surgery
PTK( Phototherapeutic keratectomy ) is a surgical procedure that utilises UV light and laser technology to reshape and repair the cornea. PTK has been applied to treat repetitive erosions and corneal dystrophies like map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy and basal membrane dystrophy. It helps prevent or postpone corneal replacement.
- Corneal Transplant Surgery
A cornea transplant is a common way to prevent corneal problems. Corneal transplant surgery removes the infected portion of the cornea and substitutes it with healthy donor tissue.
However, most people who need a cornea transplant experience a newer procedure termed lamellar keratoplasty. In this procedure, the surgeon selectively eliminates and substitutes the diseased layer of the cornea and leaves the healthy tissue in place. Replacing only infected layers with a donor graft leaves the cornea more structurally unimpaired and points to a lower rate of complications and better visual development.
- Artificial Cornea
A keratoprosthesis is an artificial cornea. A KPro can be the only choice possible for people who have not had benefit with corneal tissue implants or who possess a high risk of tissue rejection
The Boston type-1 KPro is the commonly used keratoprosthesis.
All of the above surgeries cost are not much high and can be cured of the mentioned surgeries. Now, the cost of corneal transplant surgery varies within Rs 50,000 – Rs 1 lakh and is done at private sector hospitals only. With the introduction of the eye bank, the health department will make corneal transplant facility open to needy patients free of cost.
Conclusion
The cornea covers the pupil i.e the opening at the centre of the eye, iris i.e the coloured portion of the eye and anterior chamber i.e the fluid-filled in the interior of the eye. It is responsible for focusing the maximum of the light entering into the eye.
It also tends to correct itself instantly from minor abrasions. Though, deeper abrasions may create scars to appear on the cornea, which begins the cornea to lose its transparency, leading to visual impairment. But all the cornea problems can be corrected from surgery.
If you are searching for the best eye hospital in Delhi for cornea problems treatment, Eyemantra is the best hospital to visit. They provide valuable services with discounts and the expert team will provide the quality of eye care. We offer various services like Cataract surgery, Retina Surgery, Cornea Surgery and many more. Consult our ophthalmologist now!
Book an appointment with us by ringing at +91-8851044355 and you can even mail us at eyemantra1@gmail.com.
“Eyes are the most sensitive part of the body, get them operated as soon as possible.”
