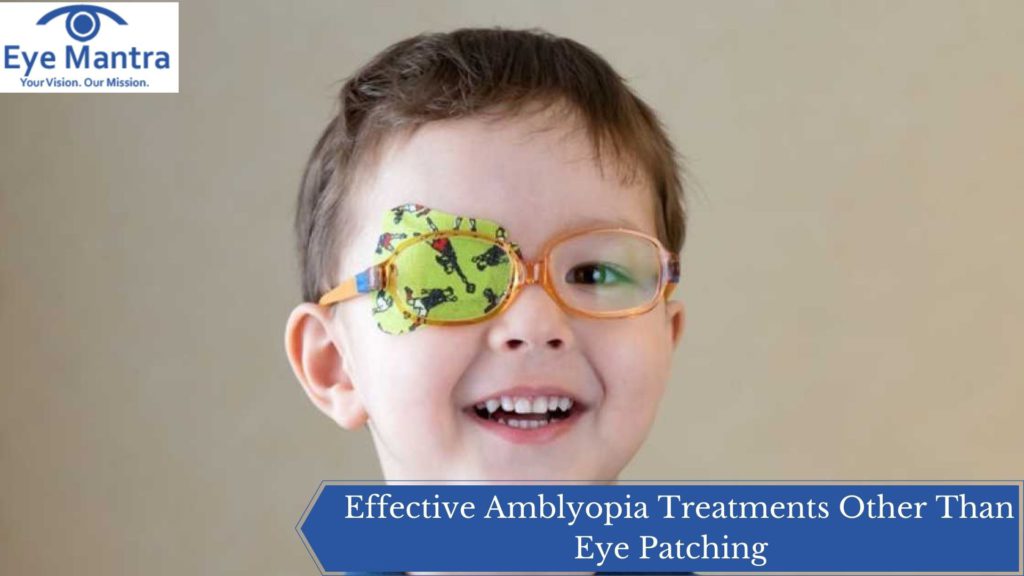
The most effective way of treating amblyopia is eye patching. There are also other options that have similar effect on the lazy eye.
Contents
What Is Amblyopia?
Amblyopia (also called as lazy eye) is a condition of the eye where the brain fails to take input from one of the eyes. It takes input from the active eye and ignores the so called lazy eye.
This condition majorly occurs in stages of early childhood ( up to 7 years of age) when the nerve pathways between one of the eyes and the brain aren’t properly stimulated. As a result, the brain tends to follow the pathway of the other eye. If not treated properly on time, the lazy eye might never get back to normal vision. The brain will then always favour one of the eyes and the second eye will never be able to participate in receiving and processing visual stimuli.
What are the ways to treat Amblyopia?
The key principle involved in the treatment of amblyopia is forcing the brain to focus on the lazy eye so that the nerve pathway that has been working lethargically might get activated and start processing inputs like the other eye.
There are a variety of treatment options available in the case of Amblyopia- eye patching, using corrective lenses, using prescribed eye drops, eye muscle surgery etc.
Treatment Options For Amblyopia – Use Of Eye Patches
Since this condition is most prominently found in children of very young ages, the treatment methods need to be such that the children can follow them easily without getting disturbed.
Out of a number of treatment options, the one option that is generally adopted by both the doctors and the parents for treating amblyopia is the use of eye patches. Covering the lazy eye of the patient with eye patches continuously for a considerable period of time helps the brain and the nerves connecting the brain to the lazy eye to get activated and start working and processing images. In 25% of the cases, discontinuation of the use of eye patches can pose risk of amblyopia returning to the children.
In such cases, children with amblyopia must wear an eye patch over the stronger of the two eyes. The patch is worn for 2–6 hours a day while the child is awake for several months or years, depending on the seriousness of the child’s condition.
There are two types of eye patches:
- One that is designed for the children who do not wear glasses. It works like a band-aid and is placed directly over the stronger eye.
- One that is designed for the children who wear glasses. It is a cloth patch that fits securely over one lens.
Making sure that your child wears the eye patch and that too properly and continuously for the said time period can be a huge challenge. But kids usually adapt well and fast, and the patch simply becomes part of their day. In the meantime, recreational activities such as distraction with a new or exciting toy, a trip to the park, or just playing outside can help kids forget that they’re wearing an eye patch.
If due to some reasons, the eye patches are not being used by the patient properly, the brain might again tend to ignore the lazy eye and will always, like before begin to process images of the objects through one eye alone.
Amblyopia Treatment- Alternative Ways Other Than The Use Of Eye Patches
Although the method of using eye patches for treating amblyopia is proven to be quite effective in children. But, the use of eye patches is still not followed properly by some children with a lazy eye. And since, the condition majorly develops in children, it is important to figure out other ways of treating amblyopia if the children are continuously resisting the use of eye patches due to some reason or the other.
The use of Atropine eye drops
Atropine drops or atropine ointment is instilled in the non-amblyopic eye of the patient for treating Amblyopia. Atropine eyedrops, when administered to the healthy eye, have been found to improve the visual activity of the eyes with moderate amblyopia. A study had recently been conducted that involved two clinical trials. The trials enrolled children of age 3 to 12 years with moderate amblyopia. In each of the trials, otherwise eligible subjects who had severe amblyopia had also been enrolled to explore and examine the effectiveness of weekend atropine treatment for severe amblyopia.
Atropine 1% eye drops help in blocking parasympathetic innervation to the ciliary muscles and to the pupil of the eye, causing pupillary dilation and temporary loss of accommodation (the ability to focus at nearer objects). Since it removes the ability to accommodate, atropine is more effective in farsighted eyes; in such eyes, it does not allow the child to focus at objects near to him.
The main aim of using Atropine is to stimulate preferential near fixation of the amblyopic eye and hence leading to visual improvement. The studies conducted concerning Amblyopia Treatment have also demonstrated that using atropine on weekend basis provides an improvement in visual acuity similar to that of daily use of atropine when treating moderate amblyopia in children of 3-7 years of age.
One study was conducted to examine the combined effect of eye patching and the atropine eye drops when taken up by children of age 7-12 years, to speed up the treatment process. By the end of the study, most clinicians decided not to prefer amblyopia treatment by combining eye patching and atropine eye drops.
Bangerter filter
A less utilized treatment option is the use of Bangerter filter. In this treatment option, a graded translucent adhesive is applied to the child’s glasses over the lens of the non-amblyopic eye, producing a blurred image. The healthy eye infers a blurred image in front of it and hence the lazy eye is forced to form a clear image of the object. Children who cannot tolerate eye patches due to some reason or the other may get the same results by using Bangerter filters. Bangerter filters are a kind of opaque covering that fits on the inside of the eyeglass lens worn over the healthy eye.
Unlike the eye patches, Bangerter filters should be worn full time. They can be modified according to the density and opaqueness with time, as the condition of the lazy eye improves. For this reason, they may be useful after patching has occurred, as a secondary treatment option. These filters are mostly used in children of older age who prefer a less noticeable option than eye patching.
Use of occlusive contact lenses
The use of occlusive contact lenses is an effective option for the treatment of amblyopia. These lenses block vision in the non-amblyopic eye. Approximately 30% of the enrolled patients in one study successfully wore an occlusive contact lens. The study also included infants and young children.
Generally, it is advised to wear occlusive lenses for less than 10 hours per day. This reduces the chance of occlusion amblyopia of the non-amblyopic eye to a great extent. When using occlusive contact lenses, we must monitor the corneal health of the patient related to contact lens wear. Occlusive contact lenses can be more effective in children who are already using contact lenses. Otherwise, it requires additional help from the parents in encouraging and convincing their children for using contact lenses with care. The parameters of an occlusive lens are determined by fitting a clear lens of the same design as the opaque lens.
The best way to treat your eyes is to visit your eye care professional and get your eyes checked regularly. He will be able to assess the best method of treatment for your eye ailment. Visit our website Eyemantra.
To book an appointment call at +91-8851044355. Or mail us at eyemantra1@gmail.com. Our other services include, phaco surgery, Cataract Surgery, and many more.
Related Links
Antibiotic Eye Drops: Used For Treatment Of Bacterial Eye Infections