Contents
DEFINITION OF THE RETINA:
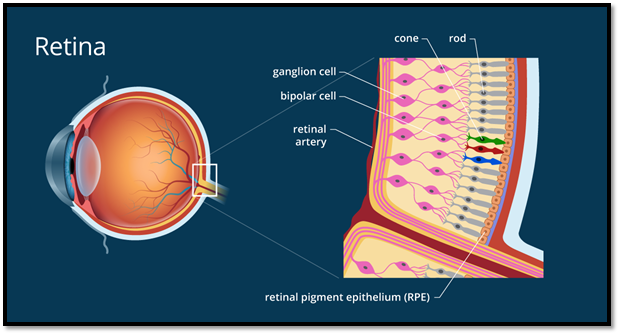
The retina is a light-delicate layer that lines at the back of the eye. It’s about 0.2 mm thick and is nearly the size of a silver dollar. The retina is comprised of 200 million neurons, a large number of which are photoreceptors. Photoreceptors assimilate light and afterward change over and communicate those signs through the optic nerve to the cerebrum.
There are two fundamental types of photoreceptors, rods, and cones, inside the retina. The fovea inside the macula, which might be a focal space of the retina, has the most elevated centralization of cones however not one single rod. 2 Cones convey a better picture. The fringe of the retina then again has numerous rods, and these kinds of photoreceptors are better identifiers.
RETINAL LAYERS:
The vertebrate retina has ten particular layers:
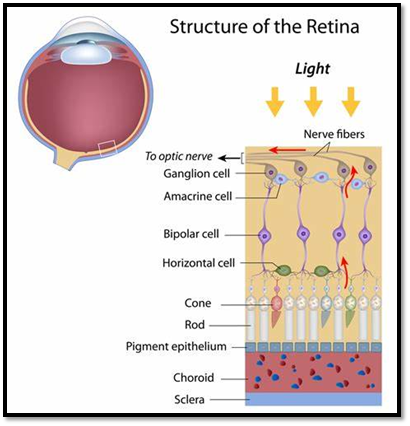
- Inner restricting layer – storm cellar film expounded by Müller cells.
2. Nerve fiber layer – axons of the ganglion cell bodies
3. Ganglion cell layer – contains cores of ganglion cells, the axons of which become the optic nerve strands, and some dislodged amacrine cells.
4. Inner plexiform layer – contains the neurotransmitter between the bipolar cell axons and the dendrites of the ganglion and amacrine cells.
5. Inner atomic layer – contains the cores and encompassing cell bodies (perikarya).
6. Outer plexiform layer – projections of rods and cones finishing off with the rod spherule and cone pedicle, individually. These make neural connections with dendrites of bipolar cells and even cells. In the macular locale, this is regularly alluded to as the Fiber layer of Henle.
7. Outer atomic layer – cell assemblages of rods and cones.
8. External restricting film – layer that isolates the inward section parts of the photoreceptors from their cell cores.
9. Inner fragment/external section layer – internal portions and external sections of rods and cones. The external portions contain an exceptionally specific light-detecting contraption.
10. Retinal color epithelium – a single layer of cuboidal epithelial cells (with expulsions not appeared in outline). This layer is nearest to the choroid and gives sustenance and steady capacities to the neural retina, The dark shade melanin in the color layer forestalls light reflection all throughout the globe of the eyeball; this is critical for clear vision.
These layers are regularly assembled into 4 fundamental handling stages: photoreception; transmission to bipolar cells; transmission to ganglion cells, which likewise contain photoreceptors, the photosensitive ganglion cells; and transmission along the optic nerve. At each synaptic stage, they are added along with the side interfacing flat and amacrine cells.
ALL POSSIBLE RETINAL PROBLEMS
Basic retinal ailments and conditions include:
- Retinal tear. A retinal tear happens when the unmistakable, gel-like substance inside the focal point of your eye (glassy) pulls on the meager layer of tissue coating the back of your eye (retina) with enough foothold to cause a break in the tissue. It’s frequently joined by the unexpected beginning of side effects, for example, floaters and blazing lights.
- Retinal separation. A unit of the retina is characterized by the presence of liquid under the retina. This normally happens when a liquid goes through a retinal tear, making the retina lift away from the fundamental tissue layers.
- Diabetic retinopathy. If you have diabetes, the minuscule veins (vessels) in the back of your eye can fall apart and release liquid into and under the retina. This makes the retina swell, which may obscure or mutilate your vision. on the other hand, you may grow new, unusual vessels that break and drain. This additionally declines your vision.
- Epiretinal layer. The epiretinal film is a fragile tissue-like scar or layer that seems like crinkled cellophane lying on the head of the retina. This layer pulls up on the retina, which mutilates your vision. Articles may seem obscured or slanted.
- Macular opening. A macular opening is a little imperfection in the focal point of the retina at the rear of your eye (macula). The opening may create from unusual footing between the retina and the glassy, or it might follow a physical issue to the eye.
- Macular degeneration. In degeneration, the focal point of your retina starts to fall apart. This causes manifestations like obscured vision or a vulnerable side in the focal point of the visual field. There are two sorts — wet degeneration and dry degeneration. Numerous individuals will initially have the dry structure, which can advance to the wet structure in one of the two eyes.
- Retinitis pigmentosa:- Retinitis pigmentosa is an acquired degenerative malady. It gradually influences the retina and causes loss of night and side vision.
Normal RETINAL TESTS:
- Demonstrative B-filter
A B-filter is an ultrasound machine used to see the inner structures of the eye. With the B-examine, the eye doctor can see a cross-part of the eye. It is utilized while, during an expanded test. It can also be utilized to find and follow malignant tumors and different anomalies.
Symptomatic A-Scan
Like the B-check machine, an analytic A-filter is an ultrasound machine. While the B-examine gives a perspective on the cross-segment of the eye, the A-filter gives a perspective on the top segment. The symptomatic A-filter permits the professional to figure the size of a store inside the eye.
Fluorescein angiography is a typical test used to analyze and screen the effect of diabetic retinopathy and macular degeneration. Fluorescein angiography is an asymptomatic technique that utilizes an uncommon camera to take photos of the progression of the retina, the light touchy tissue in the rear of the eye. The photos are communicated to a PC, permitting your PCP to see a progression of advanced retinal pictures.
To plan for a fluorescein angiography test, you will get enlarging drops to extend the size of your eyes, taking into consideration a simpler perspective on the rear of your eye. An attendant will at that point infuse a vegetable-based color (fluorescein) in your arm. The color goes through the veins and into the courses that circle all through the body. As the color goes through the veins of the retina, a professional uses an uncommon camera to take roughly two dozen photos of the retina.
The principal behind this test is to uncover the state of the veins inside the retina. On the off chance that the veins in the retina are unusual, the photos will show color spilling into the retina or recoloring of the veins. Harm to the covering underneath the retina or the presence of strange fresh blood vessels developing underneath the retina may likewise be uncovered. The exact area of these anomalies can be dictated by a cautious understanding of the fluorescein angiogram by your ophthalmologist. The ophthalmologist utilizes this data to decide if extra checking, laser strategies, or infusions are justified.
There are a few dangers related to fluorescein angiography, yet the indicative advantages of the tests overwhelmingly exceed these dangers. After the color is infused, your skin may turn yellowish for a few hours. This tone vanishes as the color is shifted through the body by the kidneys. Since the color is eliminated by the kidneys, your pee will turn brilliant yellow for as long as 48 hours following the test.
A few people may encounter slight queasiness during the strategy, however, this generally passes inside a couple of moments. If the color spills out of a delicate vein during the infusion, some confined consuming and yellow recoloring of the skin may happen. This consuming ordinarily endures a couple of minutes and the recoloring will disappear in a couple of days.
Hypersensitive responses to fluorescein color are uncommon. On the off chance that they happen, they may cause a skin rash and tingling. This is normally treated with oral or injectable antihistamines, contingent upon the seriousness of the manifestations. Much more seldom, serious hypersensitive responses (hypersensitivity) can happen and be perilous.
Nerve fiber layer analyzer
A nerve fiber layer analyzer is a mechanized camera that gives a realistic and factual perspective on a patient’s optic nerve. It is regularly essentially called an OCT, which represents optical soundness tomography. Notwithstanding it’s utilization for diagnosing glaucoma, the nerve fiber layer analyzer can likewise give away from macular openings and macular edema (growing).
Visual field test
The visual field is the whole territory that an individual can see, when the eye is centered on an essential issue. It incorporates focal and fringe (side) vision. While the visual field test is utilized principally to screen glaucoma, testing focal vision is especially significant for patients in danger of macular degeneration. Furthermore, macular and optic nerve head edema (growing) can be checked with this test.
Patients regularly think that it’s hard to identify changes in their visual field since one eye may make up for visual field misfortune in the other eye.
The best way to treat your eyes is to visit your eye care professional and get your eyes checked regularly. He will be able to assess the best method of treatment for your eye ailment.
Visit our website Eyemantra.
To book an appointment call at +91-8851044355. Or mail us at eyemantra1@gmail.com. Our other services include Retina Surgery, Specs Removal, Cataract Surgery, and many more