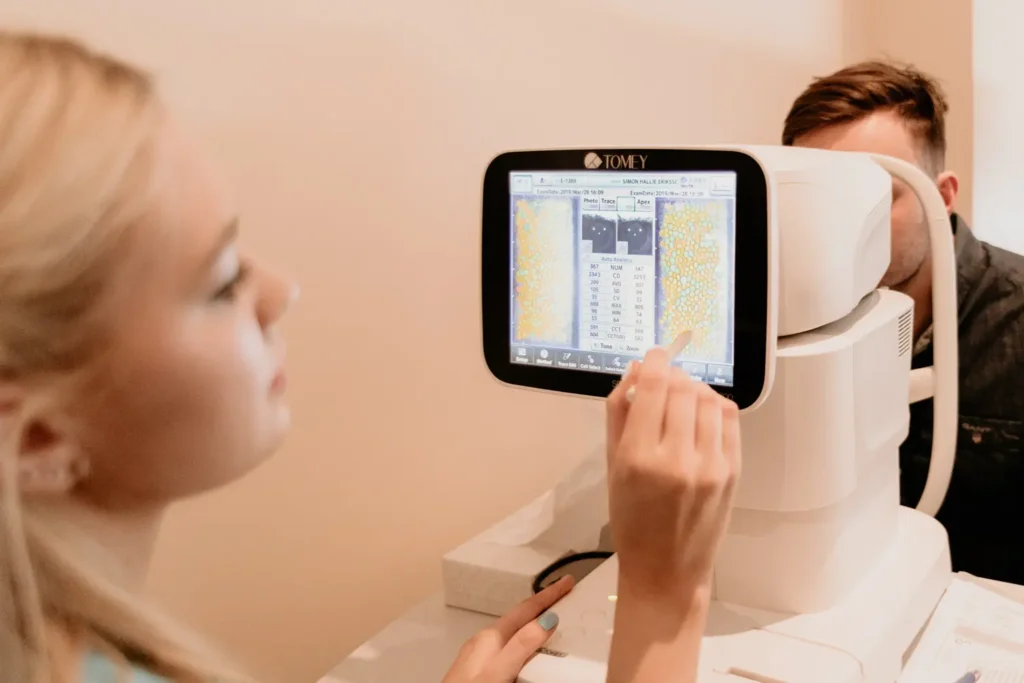
Thinking about improving your vision with ICL surgery? Before you take the leap, it’s crucial to understand the preparatory steps, specifically the essential tests required to ensure you’re a good candidate. In this blog, we’ll guide you through the key examinations and measurements that eye specialists perform before ICL surgery. So, let’s dive into what tests you’ll undergo and why they matter for your journey to clearer vision!
Contents
Essential Tests Required Before ICL Surgery
Refraction Test
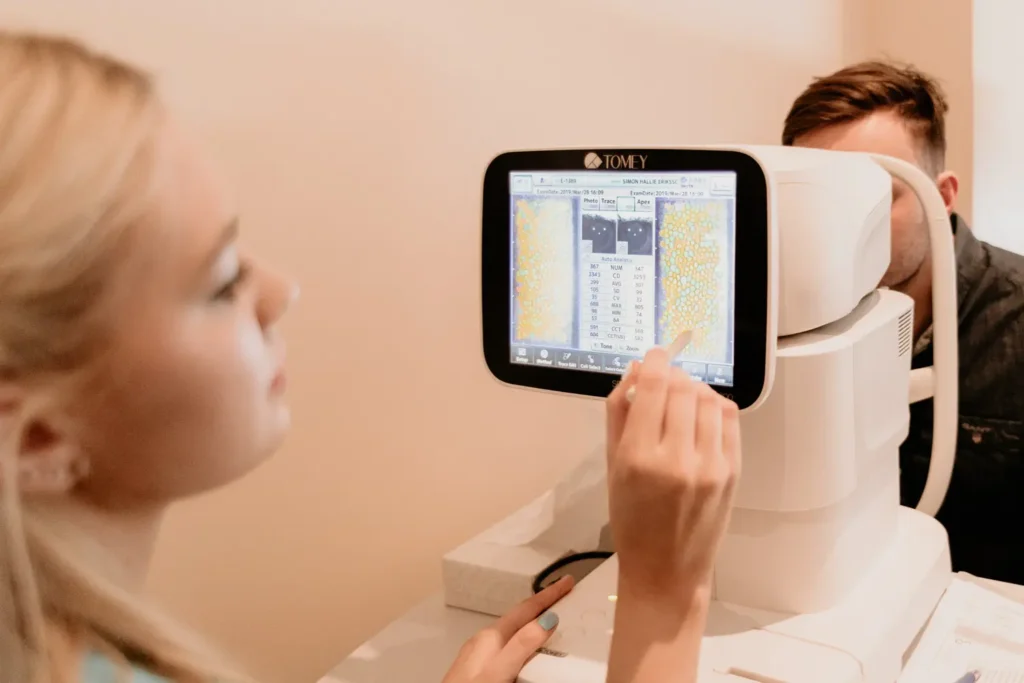

Before ICL (Implantable Collamer Lens) surgery, determining the correct prescription through a refraction test is crucial for optimal vision correction.
- Manual Refraction
This involves using a retinoscope to shine light into the eyes and observe the reflection from the retina. Various lenses are tried manually to find the one that provides the clearest vision. - Automated Refraction
This quicker, automated method uses machines to measure how light is refracted by the eye, offering a baseline prescription by assessing the light’s behavior as it enters your eye.
Importance of Dilation
Dilation is often part of this testing to ensure accuracy. It expands the pupils, allowing the eye doctor to see more clearly into the eye and better determine the full refractive error.
Accurate refraction is essential to ensure that the ICL surgery results in the best possible vision correction, emphasizing the importance of both precise measurement and patient comfort during the test.
Your Help Can Make a Difference!
With Every Donation, You’re Gifting an ICL Surgery To Someone in Need!
Corneal Pentacam
This test provides a detailed and comprehensive analysis of the cornea’s shape and structure, using advanced scanning technology to capture precise 3D images of the anterior eye segment.
Detailed Analysis
The Pentacam test utilizes a rotating camera to create a series of detailed slit images of the cornea, which are then compiled to form a complete three-dimensional map. This map includes critical measurements such as corneal thickness, curvature, and volume, providing an in-depth look at the corneal anatomy.
Anterior Chamber Depth (ACD) Measurement
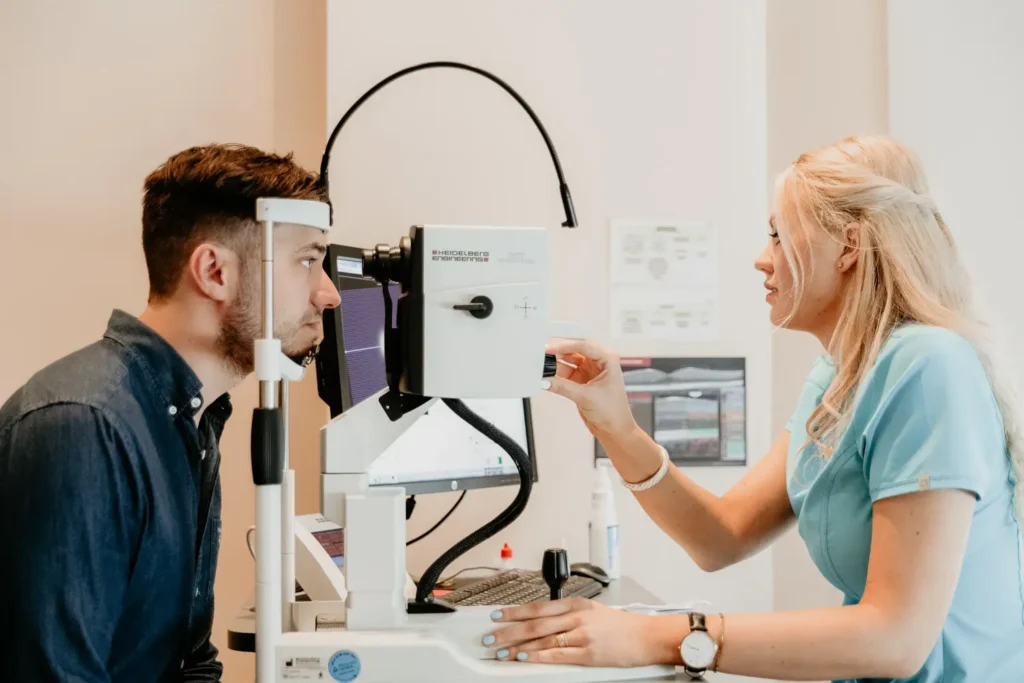

The Anterior Chamber Depth (ACD) measurement is a critical preoperative evaluation for ICL (Implantable Collamer Lens) surgery. This test measures the depth of the eye’s anterior chamber, which is the space (a minimum depth of 2.8mm) between the cornea and the iris.
Measurement Process
ACD is typically measured using optical coherence tomography (OCT) or ultrasound biomicroscopy. These technologies provide high-resolution images that allow precise measurement of the anterior chamber’s depth.
The ACD measurement is a straightforward yet vital procedure that determines whether a patient is a suitable candidate for ICL surgery, ensuring both the safety and effectiveness of the lens implantation.
Optical Biometry Test
This test plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the implanted lens will provide the best possible vision correction and fit perfectly within the eye.
Purpose and Process:
- Eye Length Measurement
Optical biometry involves the use of light waves to measure the axial length of the eye — from the front of the cornea to the retina at the back of the eye. This measurement is critical for determining the focusing power required from the ICL to correct vision accurately. - Corneal Power Assessment
The test also measures the curvature and power of the cornea. This information is crucial to calculate the total refractive power needed in the ICL to achieve optimal visual outcomes.
Pachymetry
Pachymetry is an essential diagnostic test used to measure the thickness of the cornea, providing crucial data for evaluating the suitability of a patient for ICL (Implantable Collamer Lens) surgery.
Corneal Thickness Measurement
Pachymetry is typically performed using ultrasound or optical coherence tomography (OCT) technologies. These methods provide precise measurements of corneal thickness.
White-to-White Diameter Measurement
This measurement determines the horizontal diameter of the eye’s limbus, which is the border between the cornea and the sclera. Understanding the WTW diameter is essential for selecting the right size of the ICL to ensure proper fit and function.
Purpose and Process:
- Measuring Limbal Diameter
The WTW measurement is typically conducted using calipers or more advanced imaging techniques such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) or corneal topography. These methods provide accurate measurements of the horizontal visible iris diameter, giving an estimate of the size of the eye’s internal structures.
Dilated Retinal Examination
This examination involves dilating the pupils with special eye drops to provide a comprehensive view of the retina, allowing the eye care professional to assess its health and identify any underlying conditions.
Purpose and Process:
- Expanding the View
Dilating the pupils widens the access to the back of the eye, enabling a detailed inspection of the retina, the optic nerve, and the blood vessels. - Using Ophthalmoscopy and Imaging
During the examination, tools such as an ophthalmoscope or imaging technologies like fundus photography may be used to capture detailed images of the retinal structure.
Conclusion
Preoperative tests are essential for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of ICL (Implantable Collamer Lens) surgery. These comprehensive assessments help tailor the surgery to your specific needs, addressing potential risks and optimizing outcomes. From refraction tests to detailed retinal examinations, each step is crucial in preparing for a successful procedure.
So, if you’re considering enhancing your vision with ICL surgery, trust EyeMantra to provide thorough evaluations and top-quality care. Experience clear vision—book your free appointment now at +91 9711116605.
