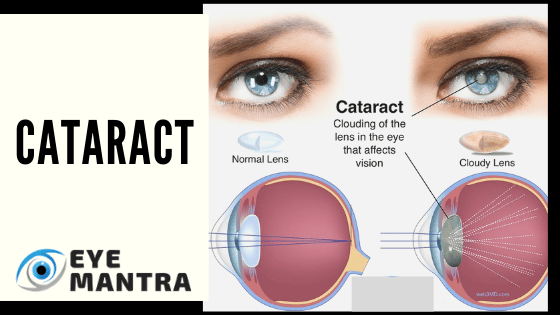
A cataract is known as the clouding of the lens in the eye which leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts usually develop slowly over time and can affect one or both eyes. The symptoms of cataracts could be faded colors, blurred vision or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and trouble seeing at night. This may result in having trouble driving, reading, or recognizing faces. Poor vision caused due to cataracts also results in an increased risk of falling and depression (you can also take online depression counseling).
Cataract surgery by eye hospital in Delhi involves the removal of the natural lens by a simple surgery. One of them is phacoemulsification. After this, an artificial intraocular lens called IOL is placed in the older lens place which returns natural and normal vision.
The cataract surgery procedure is conducted using local anesthesia, which is injected around the eye or topical anesthesia numbing drops injected into the eye.
Types of Cataract
- Subcapsular cataract:
It is called as “subcapsular” due to its formation beneath the lens capsule, which is known as small “sac,” or membrane, that encloses the lens and holds it in place. This type of cataract occurs at the back of the lens. People having diabetes/those taking high doses of steroid medications have a high risk of developing a subcapsular cataract.
- Nuclear Sclerotic Cataracts:
This is one of the most common types of age-related cataract, caused primarily due to the hardening and yellowing of the lens over time. Nuclear refers to the slow clouding of the central portion of the lens, called the nucleus. Sclerotic refers to the hardening, of the lens nucleus. Nuclear cataracts usually are associated with aging.
- Cortical cataract:
A cortical cataract occurs in the lens cortex, which is the part of the lens that surrounds the central nucleus. Cortical refers to the white cloudy areas, that develop in the lens cortex. Cortex is the peripheral (outside) edge of the lens. Change in the water content of the lens fibers creates clefts, or gaps, that look like the spokes of a wheel pointing from the outside edge of the lens in toward the center.
Causes of Cataracts
There are several causes of cataracts. The reasons are as follows:
- Age:
Age is the most common reason for cataracts. The lens proteins denature and degrade over time causing it to harden. This process is further accelerated due to diseases like diabetes and hypertension. The environmental factors, including toxins, radiation, and ultraviolet light are also responsible for cataracts. The eye care in elderly age is important for having a clear and healthy vision.
- Smoking:
Cigarette smoking has shown to double the rate of nuclear sclerotic cataracts and triple the rate of posterior subcapsular cataracts.
- Due to the UV ultraviolet radiation:
Cataracts can arise due to exposure to various types of radiation. X-rays, a form of ionizing radiation, can damage the DNA of lens cells. Ultraviolet light, specifically UVB, has also been shown to be a reason for cataracts. The protein coagulation caused by electric and heat injuries whitens the lens. This is the same process that makes the clear albumin of an egg white and opaque during cooking.
- From long-term use of steroids and other medications:
Some medications may increase the risk of cataract development. Corticosteroids most commonly cause the posterior subcapsular cataracts. People with schizophrenia often have the risk for lens opacities (such as diabetes, hypertension, and poor nutrition). On the other hand, antipsychotic medications are unlikely to contribute to cataract formation. Miotics and triparanol may increase risk.
- Because of Injury:
Injury can cause swelling, thickening, and whitening of the lens fibers. While the swelling normally resolves with time, but the white color may remain. In severe trauma, or in injuries that penetrate the eye, the capsule in which the lens sits can be damaged. This damage allows fluid from other parts of the eye to enter the lens resulting in swelling and then whitening, obstructing light from reaching the retina at the back of the eye. Cataracts may develop in 0.7% to 8.0% of cases following electrical injuries.
Tips for Preventing Cataracts
- See your eye doctor regularly:
Even if your vision is clear and healthy, make it a priority to schedule yearly eye exams with your eye doctor. Regular eye checkups can help you to have an eye care professional to look for signs of cataracts, glaucoma, macular degeneration, and other vision disorders. Early detection may save your sight. Especially after the age of 40 years or above.
- Eat a diet rich in beneficial nutrients:
There are several antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that can help you in reducing the risk of developing cataracts. A 2008 study of 35,551 women found that those who consumed the most lutein and zeaxanthin (antioxidants found in yellow or dark-green leafy vegetables), had an 18% lower chance of developing cataracts than those who consumed the least amount of lutein and zeaxanthin. In another study done in 2005, it was found that omega-3 fatty acids help in shielding your eyes from cataract development. A healthy diet should be a priority for all of us. Eye Nutrition is as important as a healthy diet for your body.
- Quit smoking:
We all know that cigarettes pose a bad effect on health to you and those around you. Research shows that smoking doubles your chances of developing cataracts and the risk continues to grow based on how much you smoke.
- Cut back on the Alchohol:
Remember to enjoy your beer, wine or cocktails in moderation. Like cigarettes, excess alcohol consumption can have several health risks, including an increased chance of developing cataracts.
- Protect those eyes from the sun:
A 2014 John Hopkins study verified that years of chronic sunlight exposure could increase your risk of cataracts. Make sure you wear a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses with UV protection when outside for extended periods.
- Keep your diabetes under control:
Data suggests that those with diabetes are at a greater risk for developing cataracts. That is why maintaining healthy blood sugar is so important—for both your overall health and the health of your vision.
- Avoid using corticosteroid medications for any length of time:
The Long-term consumption of oral steroids is a well-known cause of cataracts. Always ask your doctor about risk factors when starting a new drug regimen.
If you are feeling the first signs of cataract or you are starting to have a blurred vision get in touch with our doctors now. Call +91-8851044355 now to book an appointment. Or email at eyemantra1@gmail.com.
If you are looking for a good eye hospital in Delhi. If your looking for any surgery related to eyes do visit our website Eyemantra. We offer various services like Retina Surgery, Cataract Surgery, Specs Removal, and many more.
Related Posts: